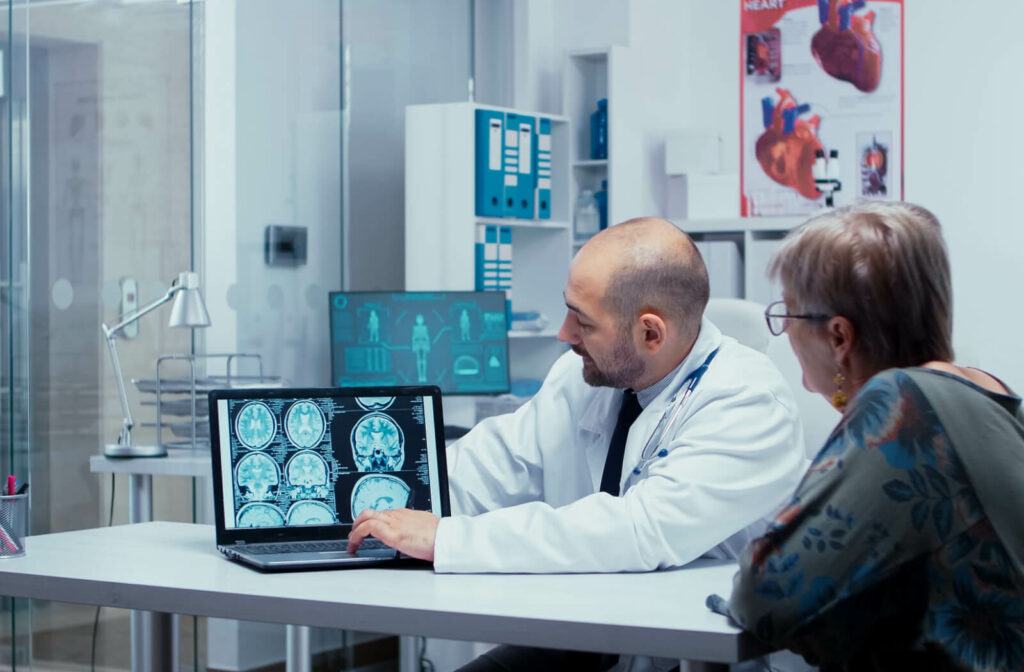
Do you know the signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease? Many people think only elderly individuals get it, but it can affect adults at any age. It is important to be aware of this disease and its effects on the brain so that early diagnosis can take place if needed.
The anatomy of a brain affected by Alzheimer’s is complex, with cognitive and memory changes, structural changes occurring throughout the brain, and the development of plaques and protein tangles between neurons.
Here, we’ll dive deeper into how Alzheimer’s alters a person’s neurological structure and functions once they have been diagnosed with the condition and the options you have for the care of a person with Alzheimer’s.
Overview of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s Disease is a progressive brain disorder that affects memory and cognitive function. It is the most common form of dementia, affecting millions of people worldwide. The disease is named after Dr. Alois Alzheimer, who discovered it in 1906.
It starts with mild memory loss and gradually progresses to impairing the person’s daily routine and social skills. It’s a disease that can take an emotional toll on the person diagnosed with it and their family members.
Although there is no cure for Alzheimer’s Disease, medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications can help manage the symptoms and improve the person’s quality of life. Learning about the disease, its risk factors, and how to manage it can make a significant difference in how it affects those we care about.
Anatomy of a Brain with Alzheimer’s
The human brain is a fascinating organ responsible for controlling our thoughts, feelings, and movements. However, when Alzheimer’s disease sets in, the brain undergoes significant changes that impede its normal operation. Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects primarily memory and cognitive functions.
A brain with Alzheimer’s shrinks or atrophies, causing neurons to die and plaques to accumulate in areas such as the hippocampus. The hippocampus is the part of the brain responsible for memory and thinking. The brain may change slowly, and therefore, Alzheimer’s may not be detected by an MRI. Over time, as the brain atrophies, this leads to symptoms of Alzheimer’s manifesting.
Therefore, it is crucial to understand the anatomy of a brain with Alzheimer’s to develop effective treatments and therapies that can alleviate its symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients.
Changes in Cognition & Memory in an Alzheimer’s Brain
As we age, it’s common for our memory and cognitive abilities to decline, but for those with Alzheimer’s disease, these changes can be much more severe. Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive disorder that affects the brain, leading to a decline in memory, thinking, and, eventually, the ability to carry out even the simplest tasks.
As the disease progresses, the brain undergoes changes that make it increasingly difficult for individuals to remember recent events, communicate effectively, and make decisions.
Structural Changes to the Brain Caused by Alzheimer’s
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex is the brain’s outer surface and is responsible for intellectual functioning. The cerebral cortex atrophies (shrinks) and develops amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. The plaques are on the outside of neurons, which are the brain’s nerve cells.
Changes in the Brain Folds
Using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), you can detect two things. One is the brain substance in the gyri (folds of the brain) is decreased. The second is the sulci (spaces in the brain’s folds), which are enlarged. This is just one noticeable change in a brain with Alzheimer’s.
Neurofibrillary Tangles
The neurofibrillary tangles are composed of Tau proteins, which play a crucial role in the standard structure and function of the neuron. In people with Alzheimer’s disease, the initially straight Tau proteins mutate due to overactive enzymes, resulting in twisted strands that clump together and become tangles that accumulate inside the neuron. They further disrupt cell activity, such as altering the movement of nutrients, and result in neuron death.
Beta-Amyloid Protein Plaques
It is believed that beta-amyloid also plays a role in causing these tangles. These proteins collect between neurons and cause further disruption in cell activity. These plaques are made up of B-amyloid protein derived from a larger protein called Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP).
Unfortunately, at the moment, the purpose of APP is unknown. We do, however, know that it takes one of two pathways. One leads to normal functioning, while the other results in changes in the brain, as seen in Alzheimer’s.
More research is needed at this time to determine the cause of these plaques and APP’s effects on a brain with Alzheimer’s.
Strategies to Support Cognitive Health for Those with or without Alzheimer’s
As we age, it’s natural to worry about cognitive health. And for those with Alzheimer’s disease, cognitive decline can be especially concerning. Fortunately, there are strategies you can use to support cognitive health and potentially slow the progression of Alzheimer’s. But these strategies aren’t just for those with Alzheimer’s; they’re helpful for everyone!
Engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and participating in brain-stimulating activities like puzzles or games can all contribute to cognitive health. By making these strategies a regular part of your life, you could support your brain’s health for years.
For the Future of Your Loved One
Alzheimer’s Disease is a devastating diagnosis for any individual and their family. As research continues to uncover more about the disease, medical professionals strive to understand how to best assess and treat individuals diagnosed.
Even for those who struggle with Alzheimer’s, there are experts ready to assist in providing them with the appropriate care and support they need. The Fairway at Naples understands this dynamic and has trained experts who can give your loved one the care they need. Contact us today to schedule a tour so you can check out our community in person and help your loved one receive the kindness, respect, and quality of life they deserve.